We've captured the standout insights from the event series in an investor-ready eBook.


Report
During market volatility, high-quality bonds have historically demonstrated their value as portfolio stabilisers.
High quality bonds are in the spotlight as recent developments in global financial markets have highlighted persistent challenges in the international investment landscape. Current factors creating market uncertainty include:
As we have witnessed, markets typically react adversely to uncertainty which can result in significant losses in equity markets amid heightened volatility. Factors such as leverage, lack of liquidity and the dash for cash can lead to severe movements in asset prices during these times.
In commodity markets, substantial price fluctuations often occur during volatile periods, with energy and industrial metals particularly vulnerable to variation. Fixed income markets have been modestly affected, mostly in the corporate bond and hybrid space, with a widening of credit spreads pushing down capital prices approximately 1-1.5% for investment grade rated instruments. Sub-investment grade bonds fared worse, with wider credit spread widening pushing down capital prices by approximately 3.5%. Government bond yields (and capital prices) have remained relatively stable.
The following table represents the price change percentage (%) in key asset classes for the period 26 March – 9 April 2025.
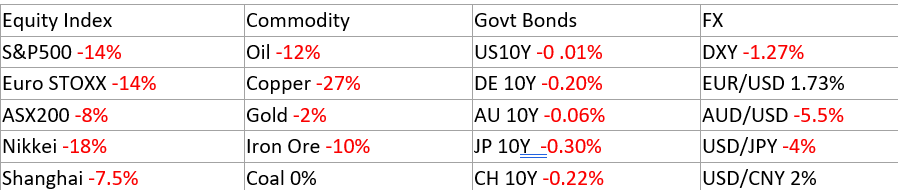
Most notably, during periods of high volatility, fixed income assets (i.e., government bonds and high-quality corporate bonds) experience smaller price changes when compared to equity and commodity markets. This pattern has been consistent across multiple historical market correction events, including the 2008 financial crisis, the 2020 COVID market crash, and other significant downturns.
When market uncertainty arises, investors typically seek safer assets—a phenomenon known as “flight to quality.” This increased demand for government bonds tends to push their prices up and yields down. Additionally, during economic uncertainty, inflation expectations and growth forecasts often decline, further supporting bond prices. This counter-cyclical behaviour is what makes bonds valuable portfolio stabilisers.
Diversification is a key investment strategy designed to reduce risk and improve the stability of returns by spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, regions, and financial instruments. The objective is to create a smoother total return for an investment portfolio. By holding a variety of investments that are not closely correlated, an investor can reduce the overall volatility of their portfolio and protect against significant losses in a single area.
While bonds offer significant portfolio benefits, investors should also understand their potential drawbacks such as:
Investors can access bonds through several vehicles including:
Bonds provide a combination of stability, predictable income, and diversification. As part of an investment portfolio, bonds can play an important part in balancing risk and return. The appropriate allocation to bonds depends on factors such as investor risk tolerance, investment time horizon, income needs, and overall financial objectives.
NAB’s Global Bond Service provides wholesale investors with direct access to bonds with highly rated issuers including Federal government, State government and corporations (including banks and insurers).
To discover more call 1300 683 106 or email us on investordesk@nab.com.au
The information contained in this article is believed to be reliable as at April 2025 and is intended to be of a general nature only. It has been prepared without taking into account any person’s objectives, financial situation or needs. Before acting on this information or acquiring any product or service, NAB recommends that you consider whether it is appropriate for your circumstances. NAB recommends that you seek independent legal, property, financial and taxation advice before acting on any information in this article.
©2025 NAB Private Wealth is a division of National Australia Bank Limited ABN 12 004 044 937 AFSL and Australian Credit Licence 230686.
The information contained in this article is intended to be of a general nature only. It has been prepared without taking into account any person’s objectives, financial situation or needs. NAB does not guarantee the accuracy or reliability of any information in this article which is stated or provided by a third party. Before acting on this information, NAB recommends that you consider whether it is appropriate for your circumstances. NAB recommends that you seek independent legal, property, financial and taxation advice before acting on any information in this article. You may be exposed to investment risk, including loss of income and principal invested.
You should consider the relevant Product Disclosure Statement (PDS), Information Memorandum (IM) or other disclosure document and Financial Services Guide (available on request) before deciding whether to acquire, or to continue to hold, any of our products.
All information in this article is intended to be accessed by the following persons ‘Wholesale Clients’ as defined by the Corporations Act. This article should not be construed as a recommendation to acquire or dispose of any investments.
© National Australia Bank Limited. ABN 12 004 044 937 AFSL and Australian Credit Licence 230686.